
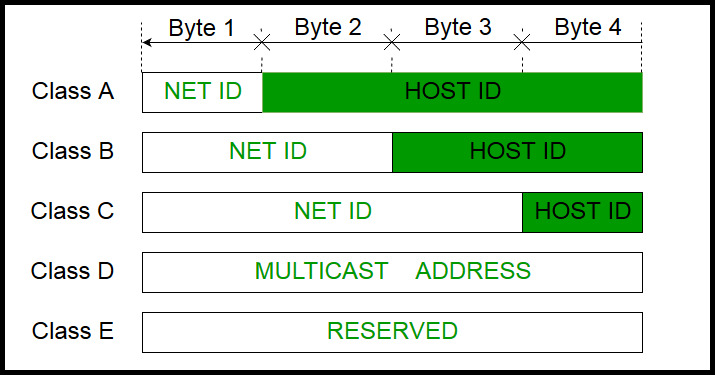
Octet 4 (8 bits) is for local subnets and hosts - perfect for networks with less than 254 hosts. The Class C example in Figure 1 has a major network address of 192.0.0.x. In a Class C address, the first three octets are the network portion. Class B addresses are used for networks that have between 24 hosts. Octets 3 and 4 (16 bits) are for local subnets and hosts. In a Class B address, the first two octets are the network portion, so the Class B example in Figure 1 has a major network address of 128.0.0.x. Class A addresses are used for networks that have more than 65,536 hosts (actually, up to 16777214 hosts!). Octets 2, 3, and 4 (the next 24 bits) are for the network manager to divide into subnets and hosts as he/she sees fit. In a Class A address, the first octet is the network portion, so the Class A example in Figure 1 has a major network address of 1.0.0.x - (where x can go from 0 to 255). For informational purposes, Class D and Class E addresses are also shown.
Figure 1 shows the significance in the three high order bits and the range of addresses that fall into each class. Given an IP address, its class can be determined from the three high-order bits (the three left-most bits in the first octet). These terms are rarely used in the industry anymore because of the introduction of classless interdomain routing (CIDR). Note: Also note that the terms "Class A, Class B" and so on are used in this document in order to help facilitate the understanding of IP addressing and subnetting. This document focuses on classes A to C, since classes D and E are reserved and discussion of them is beyond the scope of this document. There are five different classes of networks, A to E. These octets are broken down to provide an addressing scheme that can accommodate large and small networks. 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1Īnd this sample shows an IP address represented in both binary and decimal. Here is a sample octet conversion when not all of the bits are set to 1. This continues until the left-most bit, or most significant bit, which holds a value of 2 7. The bit just to the left of that holds a value of 2 1. Here is how binary octets convert to decimal: The right most bit, or least significant bit, of an octet holds a value of 2 0. The value in each octet ranges from 0 to 255 decimal, or 00000000 - 11111111 binary. For this reason, an IP address is said to be expressed in dotted decimal format (for example, 172.16.81.100). Each octet is converted to decimal and separated by a period (dot). The 32 binary bits are broken into four octets (1 octet = 8 bits). The address is made up of 32 binary bits, which can be divisible into a network portion and host portion with the help of a subnet mask. Understand IP AddressesĪn IP address is an address used in order to uniquely identify a device on an IP network. There are examples included to help tie everything together.
#Inetwork ip adress how to#
Learn how to assign each interface on the router an IP address with a unique subnet. If you do not plan to connect to the Internet, Cisco strongly suggests that you use reserved addresses from RFC 1918. If you have already received your legitimate address(es) from the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC), you are ready to begin. Subnet mask - A 32-bit combination used to describe which portion of an address refers to the subnet and which part refers to the host. Subnet - A portion of a network that shares a particular subnet address. If definitions are helpful to you, use these vocabulary terms to get you started:Īddress - The unique number ID assigned to one host or interface in a network. If your network is live, ensure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
/IP-address-57c75cfe5f9b5829f4a5cc35.jpg)
All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment.
#Inetwork ip adress software#
This document is not restricted to specific software and hardware versions. Prerequisites RequirementsĬisco recommends that you have a basic understanding of binary and decimal numbers. This document describes basic information needed to configure your router, such as how addresses are broken down and how subnetting works.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
